Key Takeaways
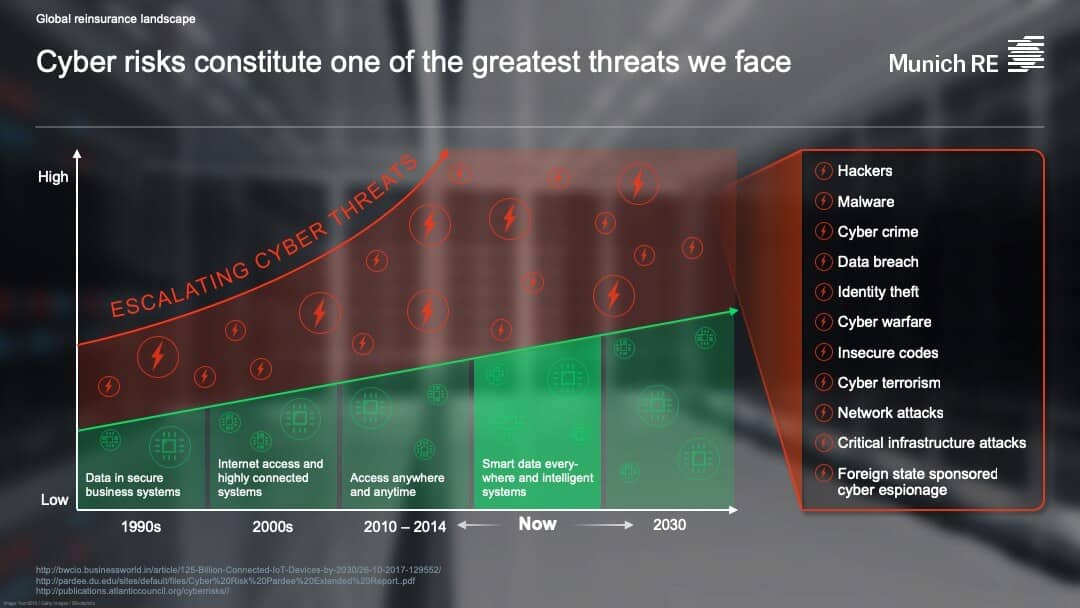
Worldwide cybercrime costs $600B USD each year. While the internet offers some of the greatest opportunities in business, it also gives rise to the greatest threats. According to the Allianz Risk Barometer 2019 study, cyber incidents and business interruption tied as the top business risks globally.
Data breaches have become a common occurrence with multiple high-profile cases:
- Yahoo continues to struggle with the fallout of a breach dating back to 2013. In early April, Yahoo agreed to pay $117.5 million in a proposed settlement.
- Quora experienced a data breach that affected 100 million users. It was caused by a third-party attack.
- Facebook’s data breaches could lead to fines under Europe’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which went into effect last year. The GDPR could apply fines of up to 4% of a company’s annual global revenue.
- Marriot experienced a hack that exposed the information of approximately 500 million customers. The hack affected the Starwood hotel system, which Marriot purchased in 2016.
- Think it only happens to massive companies? Several of our clients have experienced data breach issues as well.
What are Some of the Most Common Types of Cyberattack?
In some cases, data breaches may be tied to malware. Verizon’s 2018 Data Breach Investigations Report identified ransomware as the most common type of malware accounting for 39% of malware attacks. After infecting a computer system and encrypting the files found there, these malicious programs hold the files hostage and demand a fee for their return. The 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack is one example.
Other cyberattacks exploit human weaknesses instead of computer weaknesses. Phishing attacks work by tricking people into clicking a link or providing information. Spear phishing attacks are similar but target the victim in a more personal and convincing manner.
In business email compromise attacks, criminals pose as legitimate partners to trick employees into sending wire transfers. In 2017, business email compromise attacks cost $675 million is adjusted losses, according to the FBI. The SEC has investigated “whether certain public issuers that were victims of cyber-related frauds may have violated the federal securities laws by failing to have a sufficient system of internal accounting controls.”
Which Companies have the Greatest Cyberattack Risk?
Think your company is safe? Don’t be so sure. Cyber risks can impact any business, regardless of size. According to the Insurance Information Institute, 55% of small and midsize businesses experienced a cyberattack in the previous year, and about half experienced a data breach.
All companies from small startups to global giants need to manage their cyber risks. However, only 14% of small companies consider their ability to mitigate cyber risks to be highly effective and small businesses are less likely than large ones to obtain cyber coverage.
Cyberattacks can also strike any type of company. However, certain industries have especially high risks. For example:
- Financial institutions are attractive targets for cybercriminals. According to Beazley, ransomware attacks against financial institutions increased 18% in the third quarter of 2018.
- Healthcare organizations, which have an abundance of personal data on patients, have experienced numerous data breaches in recent years.
- App-powered companies (such as Uber) are great targets for cyberthieves.
- Cryptocurrency companies face unique risks. In addition to problems arising from compliance with SEC regulations, theft of cryptocurrency has been on the rise.
What are the Fallouts of a Cyberattack?
If a cyberattack hits your company, you could face numerous problems:
- Business interruption can occur while your organization deals with malware, security issues, loss of data and the resulting fallout.
- Financial losses can result from the cost of notifying your customers and providing credit monitoring; restoration of files and computer systems; lawsuits; and regulatory fines.
- Reputation loss can occur if consumers lose trust in your company.
Is Cyber Insurance Really Necessary?
According to A.M. Best, the total number of cyber claims increased from 5,955 in 2016 to 9,017 in 2017. Cyberattacks are on the rise. As more and more businesses get hit with heavy losses, regulatory fines and expensive lawsuits, the need for robust cyber insurance is clear.
What Factors Affect Cyber Insurance Pricing?
Cyber insurance pricing varies widely depending on a number of variables. Small businesses can expect to pay anywhere from $1,000 to $7,500 for an annual premium, according to FitSmallBusiness.
Underwriting for cyber insurance is complex and evolving. To understand the factors that impact premium costs, underwriters look at the potential risks.
- Systems vulnerabilities. Hackers love to exploit vulnerabilities in software programs. Patches and updates can keep systems secure, but only if you actually apply them. Having up-to-date programs with top-of-the-line security features is essential.
- Security training protocols. Data breaches can occur when employees mistakenly expose data. Business email compromise attacks succeed when employees fall for fraudulent requests. Malware attacks spread when employees click on links they shouldn’t. All employees must be trained on how to avoid cyber risks, regardless of their position in the company.
- Loss history. Data breaches and malware attacks are increasingly common. However, a long history of repeated issues could signal security flaws. Response is also important. Companies can run afoul of regulations if they attempt to cover up breaches, making a bad situation worse.
- Types of data collected and stored. Companies that store financial details, Social Security Numbers and other types of sensitive information are especially vulnerable to hackers.
What is the Cyber Insurance Outlook for 2019?
Cyber insurance is a fast-growing market. Aon reports that the number of U.S. cyber insurers grew from 140 in 2016 to 170 in 2017, while direct written premiums went from $1.35 billion to $1.84 billion. According to A.M. Best, Chubb INA Group had $284.4 million in cyber direct premium in 2017, making it the top cyber insurer. The Hartford Insurance Group had the greatest number of cyber policies in force.
How Can Businesses Manage Cyber Risk?
Here are the main takeaways you should pay attention to for 2019:
- Keep up with tightening regulations. Make sure you’re in compliance with new laws regarding data breach notification and consumer privacy rights. The GDPR went into effect in Europe in 2018. The new NYDFS Cybersecurity Regulation impacts financial organizations and is now in effect. The California Consumer Privacy Act will go into effect in 2020.
- Beef up your security. This means updating your systems to include the latest security patches, the best anti-virus protection and encryption. It also means training your workers on how to keep data safe and avoid phishing and business email compromise scams.
- Don’t assume you’re not a target. Nobody’s immune. Even with good security measures, your company could fall victim to a data breach or other attack. Plan a good response that protects your company and your customers – and invest in cyber insurance.
- Know that cyber-readiness may impact on your credit. CNBC reports that Moody’s Corp. has announced that a company’s cyber defenses, including breach detection and response, will soon be higher priorities in the assessment of credit-worthiness.
- Get your board onboard. Because cyber security can have a massive impact on business operations and profitability, boards must provide corporate oversight. Neglecting to do so may result in D&O exposures.
- Get insured. There’s no sure way to prevent cyberattacks. Your business will eventually be hit – the only question is when. As a recent McAfee report states, “Cybercrime is relentless, undiminished and unlikely to stop. It is just too easy and too rewarding and the chances of being caught and punished are perceived as being too low.”